| |
 |
 |
| |
| Home | Project | People | Research | Education | Archive | |
 |
Chemogenomics |
[English | Japanese ] |
 |
|
  |
 |
Nobutaka
Fujii
Professor,
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
Kyoto University |
Genomic information-converging
Medicinal Chemistry Based on Chemical Proteomics
Recent advance in genome
science is providing us exponentially amplified drug targets. As such,
there has been increasing upsurge in the development of innovative platform
for genome/proteome-based drug discovery to facilitate the process thereof
from a national standpoint. This project is intended to constitute a
knowledge information infrastructure for a new frontier of chemogenomics-based
medicinal chemistry beyond genomics and proteomics in fusion of genome
science and chemistry. In order to embody the innovative axis for genome-lead
drug discovery platform, we have been engaging the genomic information-converging
approach in medicinal chemistry by integration of the following research
programs.
1) Chemical characterization of drug targets based on comprehensive functional
genomics
2) Downsizing of high molecular weight biologically active peptides/proteins
using peptide-lead conformationally restricted templates for genome-lead
drug discovery
3) Development of stereo-controlled synthetic process of peptide isosteres
based on organo-metallic chemistry for "Peptide-Nonpeptide" link.
4) Chemical dissection of the aufbau principle of 7 transmembrane-G protein
coupled receptor(7TM-GPCR) and daynamic outside-in signal transduction mechanism
thereof
5) Reconstruction of 7TM-GPCR and pharmaceutical development thereof
Herein, we summarize the recent investigations
focusing on the development of highly specific CXCR4 antagonist, the receptor
of which is relevant to several problematic diseases (cancer metastasis, AIDS,
rheumatoid arthritis, etc.), as a practical application of the above strategy
(Fig. 1). Of note, the highly specific CXCR4 antagonist, as a chemical probe,
served to disclose the many physiological and pathological functions of CXCR4
including its important role for the formation of the dark zone and light zone
appeared in germinal center of lymph node (Nature Immunology, 2004, 5:
943) A new method for the facile synthesis of membrane embedded peptides utilizing
lipid bilayer-asisted chemical ligation has been also developed aiming at the
chemical synthesis of CXCR4, which is classified to 7TM-GPCR family (Chem.
Commun, 2004: 607).
 |
|
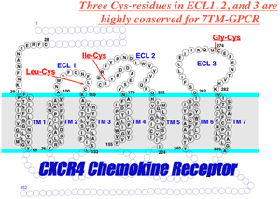 |
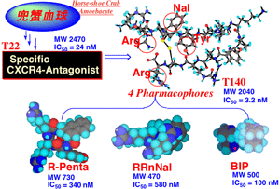
Fig. 1. Downsizing and Nonpeptidylation
of High Molecular Weight Peptides/Proteins by Conformationally-restricted
Drug Discovery Templates :Practice in Peptidic CXCR4 Antagonist
|
|
Fig. 2. Towards the Chemical
Synthesis of 7TM-GPCR |
|
Top
| 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | |
|
|

